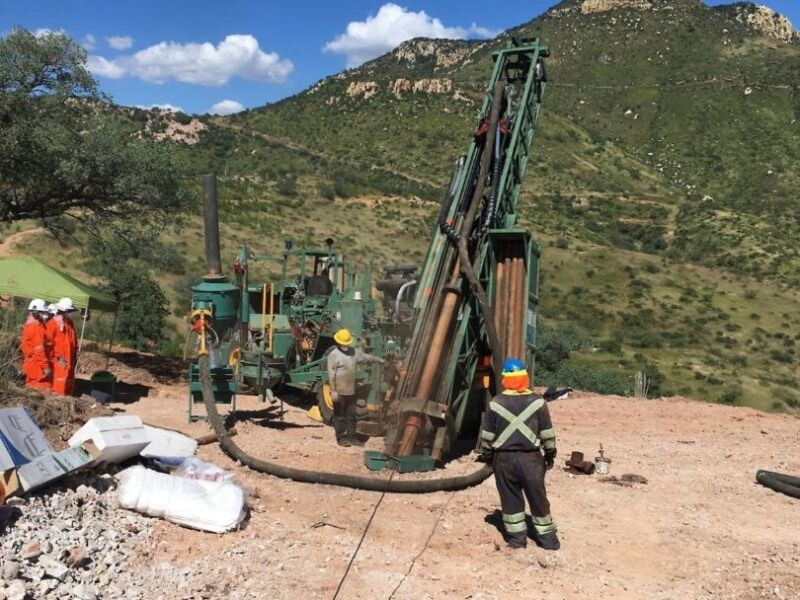
The Company’s flagship Cerro Caliche gold project is in the final permitting stage for an initial 12,000 tonnes per day open-pit, heap leach mining operation. The Company’s objective is to bring Cerro Caliche into production to fund ongoing exploration and mine expansion.
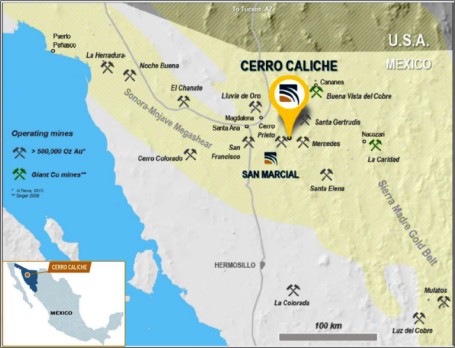
The 1,400 hectares property is strategically located in Sonora State, Mexico, between the two world-class mining districts of the Sierra Madre Gold Belt and the Sonora-Mojave Megashear. Cerro Caliche is situated close to several gold-silver mining operations, including Bear Creek Mining’s Mercedes mine and Agnico Eagle’s advanced Santa Gertrudis project, with access to a high-skilled workforce and first-class infrastructure.
Since acquiring the property in September 2018, the Company has completed 379 drill holes over 42,350 meters confirming a broadly mineralized, low-sulphidation epithermal vein structure with over 25 northwest-trending, near surface gold mineralized zones along trend. When combined with historical data, total exploration at Cerro Caliche includes over 55,300 meters of drilling, 498 drill holes and 9,739 surface samples.
Minable Resource
With only 30% of the property’s identified mineralized zones drilled and assayed to date, an updated Mineral Resource Estimate (MRE) was filed in March 2023. Prepared by SRK Consulting (U.S.) Inc. and based on a total 55,360 meters of drilled data including 498 drill holes, 17 trenches and assays for 53,865 meters of the drilled data, 65% of the combined resource tonnage is within the Indicated category and confirmed amenable to a combination of open pit mining and heap leach extraction.
MRE highlights:
Indicated Mineral Resources of 19.9Mt at 0.44 g/t Au and 3.5 g/t Ag grade; Contains within an optimized pit shell:
- 280,000 oz of Au
- 2,240,000 oz of Ag
- 290,000 ooz of AuEq
Inferred Mineral Resources of 10.5 Mt at 0.42 g/t Au and 4.0 g/t Ag grade; Contains
within an optimized pit shell:
- 140,000 ounces of Au
- 1,345,000 ounces of Ag
- 150,000 ounces of AuEq
The MRE also favorably noted the upside potential for Cerro Caliche in terms of exploration. Based on the analysis, the report outlines the exploration potential within drilled areas for Cerro Caliche to be from 15,000,000 to 22,000,000 tonnes containing:
- 120,000 to 275,000 oz of Au at 0.25 to 0.38 g/t Au
- 1,045,000 to 2,350,000 oz of Ag at 2.2 to 3.2 g/t Ag
- 125,000 to 285,000 oz of AuEq at 0.26 to 0.39 g/t AuEq
The current geological volumes and grade estimates noted above, located outside of the pit shells, are considered too limited to establish grade continuity to meet the present requirements for Reasonable Prospects of Eventual Economic Extraction (RPEEE) for the mineralized area to be considered Mineral Resources.
Preliminary Economic Assessment
The economic impact of the MRE was outlined in a new Preliminary Economic Assessment (PEA), filed in October 2023. Prepared by D.E.N.M. Engineering Ltd. and Micon International Limited, the PEA demonstrates the potential viability for a nine-year life of mine (LOM), open pit, heap leach mining operation with an initial two-year production rate of 4,000 mtpd and an increase to 12,000 mtpd for the remaining LOM.
PEA Highlights:
- Pre-Tax net present value discounted at 5% (“NPV5”) of USD $71.4 million
- Pre-Tax Internal Rate of Return (“IRR”) of 59%
- After-Tax NPV5 of USD $47.7 million with an IRR of 45%
- Gold recovery of 72% and silver recovery of 27%
- 9-year LOM with 297,575 ounces (“oz”) of gold equivalent (“AuEq”)
- LOM annual average production of 33,000 oz AuEq at 0.45 g/t AuEq
- Initial CAPEX costs of USD $15.5 million, including USD $1.83 million in contingency
- Sustaining capital costs of USD $15.5 million
- Cash(1) operating costs of USD $1,295/oz AuEq
- AISC(2) of USD $1,395/oz AuEq
- Payback period of 2.9 years
Note: All currencies are reported in U.S. dollars. Base case parameters assume $1,800/oz gold and $23/oz silver.
(1) Cash operating costs include mining, crushing, processing, assaying, and administration.
(2) All-in-Sustaining Costs include cash costs plus sustaining, refining and reclamation costs, as well as 2% royalty buyout.
Gold & Silver Price Sensitivity Analysis
| Sensitivity | $1,600 Au $20 Ag |
$1,700 Au $22 Ag |
$1,800 Au $23 Ag |
$1,900 Au $26 Ag |
$2,000 Au $28 Ag |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| After-Tax NPV (5%) | $19.14m | $33.65m | $47.68m | $62.57m | $77.02m |
| Pre-Tax NPV (5%) | $27.34m | $49.71m | $71.42m | $94.46m | $116.84m |
| After-Tax IRR | 23% | 35% | 45% | 54% | 63% |
| Pre-Tax IRR | 30% | 45% | 59% | 72% | 85% |
| After-Tax Payback | 4.1-Years | 3.4-Years | 2.9-Years | 2.6-Years | 2.4-Years |
The estimated capital costs include initial capital expenditures of USD $15.5 million for direct and indirect facility, infrastructure, EPCM and site preparation as well as sustaining capital of USD $15.5 million for crushing circuit and heap leach pad expansion, power transmission line and equipment replacement costs. Cash operating costs are estimated at USD $385.4 million or USD $1,295 per gold equivalent ounce and All-in Sustaining Costs (“AISC”) for LOM are estimated at USD $415.1 million or US$1,395 per gold equivalent ounce. Royalties include a 2% Net Smelter Return (“NSR”) buyout to certain landholders and taxes include payments to the Mexican government for mining royalty and specific mining related taxes.
Operating & Capital Sensitivity Analysis
| Sensitivity | -20% | -10% | Base Case | 10% | 20% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Costs – Pre-tax NPV (US$ million) | $128.33 | $99.87 | $71.42 | $42.97 | $14.51 |
| Operating Costs – IRR | 90% | 75% | 59% | 41% | 20% |
| Capital Costs – Pre-tax NPV (US$ million) | $76.20 | $73.81 | $71.42 | $69.03 | $66.64 |
| Capital Costs – IRR | 73% | 65% | 59% | 54% | 49% |
Capital and operating cost estimates are based on industry standards and were developed using quotes provided by mining contractors and specialists experienced in mining development in Mexico.
Exploration
With only 30% of the property’s identified mineralized zones drilled and assayed to date, Cerro Caliche has significant exploration potential. The objective of future drilling campaigns is to increase the minable resource of the project and extend the currently estimated life of mine for the proposed open-pit, heap-leach mining operation.
A proposed targeted expansion drilling campaign of approximately 9,000 meters and 56 drill holes is designed to increase the minable resource and extend the pit shells. Drilling will initially focus on the western mineralized zones where the Company plans to commence mining operations and where prior drilling demonstrated multiple high-grade ore shoots. Drilling is also planned in the northern mineralized zones to potentially increase and upgrade the resource as well as in the central mineralized zones to potentially increase the pit shell resource and reduce the strip ratio.
The Company has also identified potential resource expansion targets along the property’s northwestern corridors where prior drilling confirmed gold-silver mineralized intervals. A recent surface sampling program included 608 samples with lengths of 1.0 to 2.0 meters with assays of up to 24.8 g/t Au. The drilling program was scheduled to commence once Cerro Caliche is in production but may be moved up if permitting delays continue.
Geology
Mineralization types throughout the Cucurpe mining district include variants of epithermal low sulfidation veins and related mineralized dikes and associated volcanic domes. Local altered felsic dikes cut the mineralized meta-sedimentary rock units and may be associated with mineralization both in the dikes and meta-sedimentary rocks. The district has historically been regarded as vein dominated, but recently, open pit mining operations have been developed on disseminated and stockwork style gold mineralization.
The current interpretation of the structural and mineralization development of the Cerro Caliche project hypothesizes that a deeper intrusive stock underlays the district and is the source of mineralizing fluids and rhyolitic dikes. The interpreted normal deep faulting has provided a conduit for silica-rich mineralizing fluids, resulting in the deposition of quartz veins with gold and silver at the Project area and localization of some rhyolite dikes.
The predominant northwest trending orientation of structures is an important feature of the Project area. More than 25 strong structures with at least 200 m of strike length are counted which have generally a parallel arrangement, crossing the entire Project concession area holdings. These structures developed ahead of vein deposition and rhyolite dike intrusion which follow and fill the structures. Many veins show brecciation, which indicates movement along the structures during vein formation.
In addition to the silicification, other alteration assemblages are noted on the Project. Argillic alteration is represented as weak to moderate clay development in feldspars and the matrix of rhyolitic rocks. Limonite, consisting of hematite with lesser goethite and jarosite, is present and developed from oxidized sulphides, mainly cubic pyrite. In deeper more mafic rock types propylitic alteration is widespread.
Qualified Person
All scientific or technical information contained on this website has been reviewed and approved by Stephen Kenwood, P.Geo., a Director of Sonoro Metals Corp., who is a “Qualified Person” as defined in National Instrument 43-101 of the Canadian Securities Administrators.